Regulatory toxicology
Our customers are looking for innovative and effective ingredients for efficient formulations.
Eurosafe can offer you different solutions to meet regulatory requirements.
Thanks to an exhaustive review of regulatory and safety data available in literature, Eurosafe assists you in writing the toxicological profiles of all types of ingredients for cosmetic use.
The purpose of the toxicological profile is to identify all of the hazards inherent for a substance and to characterize the dose-response relationship on the basis of the different toxicological endpoints targeted by the SCCS.
If the toxicological data collected remain insufficient, additional in vitro test recommendations according to the established ECVAM/OECD protocols may be established.
The development of these profiles will allow you to guide the use of your cosmetic ingredients in finished products, especially for specific targets such as pregnant or breastfeeding women and babies.
The safety evaluation of a cosmetic ingredient enables to determine or validate the maximum concentration of use of an ingredient for one or several categories of cosmetics and for one or several target populations.
The cosmetic ingredient safety evaluation allow to validate the maximum concentration of use of an ingredient for one or more categories of cosmetic products and for one or more target populations.
The aim is to ensure the safe use of the ingredients under normal and reasonably foreseeable conditions of use.
Complementary to the toxicological profile, this service aims to better guide you in choosing and using cosmetic ingredients when developing new cosmetic products.
In vitro assays
Our laboratory historically specializes in in vitro studies. We offer a portfolio of assays ranging from the well-established to the most cutting-edge. Some assays are regulatory compliant to ensure safety and tolerance of finished cosmetic products.
Evaluation of the demal absorption and delivery of a test substance using excised skin
In order to evaluate the possibility of peripheral effects during dermal administration of test compounds, it is essential to evaluate these compounds’ potential transcutaneous passage.
In vitro methods measure the diffusion of chemicals across skin into a fluid reservoir.
Cryopreserved skin is used to measure diffusion only, whereas fresh metabolically-active skin is used to simultaneously measure diffusion and skin metabolism.
Such methods have found particular usage as screenings tests for comparing transcutaneous delivery of chemicals from different formulations. These methods also provide useful models for the assessment of percutaneous absorption in humans. Acceptable data from a minimum of four replicates per test preparation are required.
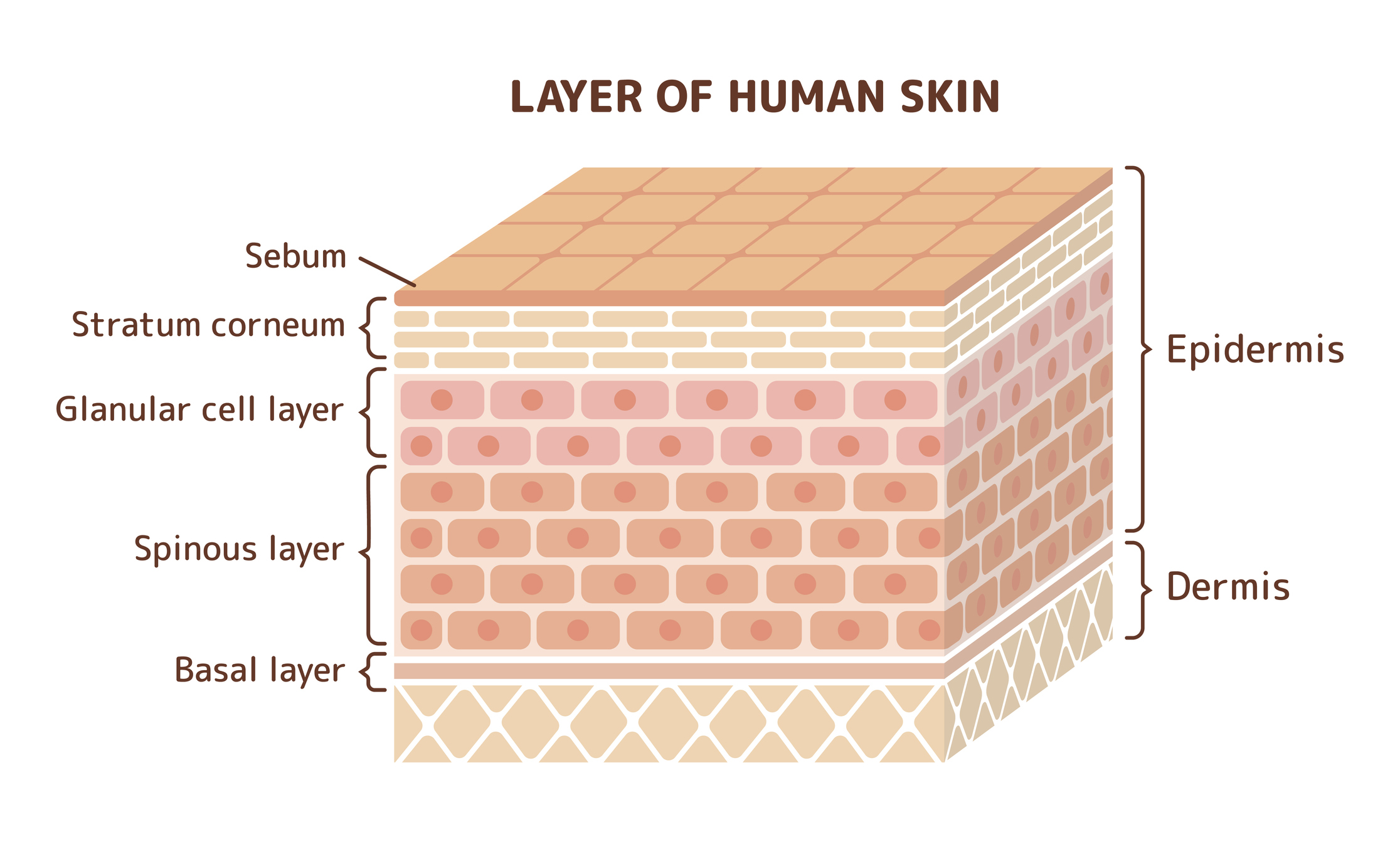
Using appropriate conditions, which are described in the OECD 428 guidelines, absorption of test compounds during a given time interval is measured by analyzing both receptor fluid and the treated skin.
The test compound remaining on the skin’s surface should be considered as absorbed unless it can be conclusively demonstrated that absorption can be determined from receptor fluid values alone.
Analysis of other components (e.g. material washed off the skin or remaining within skin layers) allows for further data evaluation, including total test substance disposition and percentage recovery.
All components of the skin should be analyzed, and recovery should also be determined. This includes rinsing of the donor chamber, skin surface, and the receptor fluid/chamber.
In some cases, the skin may be fractionated into stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis fractions for additional analysis.
Effect of the formulation on transcutaneous absorbtion of a test compound
Many requirements for an alternative non-animal test to replace the mice used within the LLNA, and represents integrated biological models that incorporate, in a fully coordinated and physiologically relevant way, all the events and processes that are needed for the acquisition of sensitization.
Eurosafe offers a complete set of standard and innovative sensitization assays which cover all key events related to the cutaneous sensitization.
Details
In silico studies/Computational toxicology
Our in silico services expedite processes of prediction of biological properties related to toxicity, activity and ADME.
We perform Physiologically based Pharmacokinetics modelings (PBPK).
Eurosafe offers services for prediction of three dimensional structure of proteins of interest by the homology modeling method using our automated state of art methods.
Homology modeling uses sequence similarity of amino acid residues with the well known 3D structure (by X ray and NMR) to predict structure of unknown protein.
The structural models are validated for quality and further optimized by Molecular Dynamics simulation. Optimized model can be used for molecular docking, macromolecular engineering and drug designing.
Homology modeling service includes:
- Sequence Alignment of Amino acids
- Prediction of 3D model
- Structure validation
- Structure optimization by MD
Eurosafe offers Molecular docking service to discover, the interaction between the protein of interest and ligand by automated high throughput screening algorithm.
It deduces the ligandability of compounds for the protein. We will report binding affinity, ligand conformation search and active site of the proteins.
On demand, the Protein-ligand complex will be further optimized by molecular dynamics simulation for interaction refinement.
Molecular Docking service includes:
- Structure preparation of Protein and Ligand
- Automated docking simulation
- Affinity prediction, ligand pose prediction and active site prediction on proteins
- Protein-ligand complex optimization by MD
Eurosafe QSAR service includes the prediction of relationships between the geometric structure of a chemical compound and biological activity.
We use QSAR methods such as OECD tool box, VEGA, Tox tree for prediction of Skin sensitization potential of the compounds according to OECD guidelines (ENV/JM/MONO(2007)2).
QSAR service includes:
- Biological properties prediction
- Skin sensitization prediction of ingredients
- Skin metabolism and sensitization prediction of ingredients
- Safety assessment of compounds
Eurosafe offers Physicochemical Based PharmacoKinetics (PBPK) modeling service to predict pharmacokinetics modeling of compounds using the validated open source software PK-SIM.
We offer PBPK service for in vitro to to in vivo pharmacological or toxicological experiments interpolation and extrapolation of knowledge between:
Effect of Dose and Exposure duration: e.g., from continuous to discontinuous, or single to multiple exposures.
Effect of Routes of administration: e.g., from inhalation exposures to ingestion.
Study Species and Individuals variation in PharmacoKinetics of compounds.
In vitro to in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) refers to the qualitative or quantitative transposition of experimental results or observations made in vitro to predicts phenomena in vivo, biological organisms.
Study of Drug Drug Interaction (DDI).
Study of ADME compartmental model predictor of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion.
Eurosafe offers service to generate customized prediction model of interest using machine learning algorithm. Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that uses sophisticated algorithms to give computers the ability to learn from the data and make predictions.
We offer in house prediction model for Bile Salt Export Pump (BSEP) protein in order to predict better ligandability of compounds by combining in-vitro data, in-silico and physicochemical properties with good accuracy.
Machine learning service includes:
- Customized prediction model
- Ligandability of compounds for BSEP


 "
"