In vitro assays
Our in vitro ADME and DMPK assays relate to solubility, in vitro metabolism, in vitro permeability and transporters, binding to proteins and bioanalysis.
Our ADME services comply with external guidelines (GLP, FDA, EMA, OECD) or are performed in a screening mode.
Eurosafe serves a number of industries including big pharma, biotech, as well as chemical and agrochemical industries.
Metabolite Profiling and Identification using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and eventually quantification.
It is well known that metabolism of a given test compound often contributes to its efficacy and toxicity observed in vivo.
Assays are standardized for:
- metabolite identification,
- metabolite profiling,
- metabolite stability,
- identification of metabolizing enzymes,
- stability in plasma and buffer (part of BCS evaluation),
- PBPK modeling
In vitro metabolism studies conducted in biological matrices ranging from isolated cells to subcellular fractions, allow the evaluation of intrinsic metabolic potential or specific mechanisms with respect to a given reaction.
Eurosafe recommends the incubation of liver, intestine and skin microsomes, as well as hepatocytes, HepaRG™, expressed enzymes, and plasma.
In addition, in vitro systems derived from various animal species permit the comparison of metabolic pathways among species (including humans) before a given compound can be tested clinically. Metabolites from Phase I and Phase II enzymes are scanned.
To test whether an investigational drug is a victim of DDIs, sponsors should use index perpetrators. Index perpetrators predictably inhibit or induce drug metabolism or transport by a given pathway and are commonly used in prospective DDI studies.
Our task:
To ensure that no development candidate fails in the clinic due to an unforeseen metabolic or pharmacokinetic property.
Our services :
- DDI induction
- DDI Inhibition
- DDI phenotyping
Details
Evaluating transporters mediated drug interaction
Membrane transporters have clinically relevant effects on the pharmacokinetics and 303 pharmacodynamics of drugs in various organs and tissues by controlling the absorption, distribution, and elimination of drugs (Giacomini, Huang, et al. 2010; Giacomini and Huang 2013).
Several transporters interact with clinically-relevant drugs. FDA guidelines.
For example:
- P-glycoprotein (P-gp or Multi-drug Resistance 1 (MDR1) protein),
- Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP),
- Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1/1B3 (OATP1B1/OATP1B3),
- Organic anion transporter 1/3 (OAT1/OAT3),
- Multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) proteins,
- Organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2).
Understanding whether a certain drug behaves as substrate or perpetrator (i.e. inhibitor or inducer) of these key transporters will help explain clinical consequences (i.e. toxicity or altered efficacy) that result from altered tissue distribution of a certain drug that functions as a substrate of a membrane transporter.
Coupled with appropriate in vitro-to-in vivo extrapolation methods such as PBPK, these assays help determine whether the sponsor should conduct in vivo drug interaction studies.
Currently, in vitro methods to evaluate transporter induction are not well understood.
Identification of the free fraction of drugs on plasma proteins, cells, or sub-cellular fractions
Eurosafe offers different approaches to evaluate plasma protein binding:
- Equilibrium dialysis method: This is the most widely used method for assessing drug binding. Non-specific fixation is kept at a minimum.
- Sharing between erythrocytes and plasma proteins: This method is applied when the test compound is lipophilic or the non-specific binding fixation is high.
Studying a drug’s binding to different plasma proteins and erythrocytes also helps evaluate its blood distribution. This distribution helps elucidate a drug’s binding capacities (NKa), and hence enables the simulation of human pathophysiological conditions.
Eurosafe performs ex-vivo studies to correlate plasma binding percentage of drug candidates (with high affinities for HDL) in 50 plasma samples (derived from a pharmacokinetic study) with concentration of a given lipoprotein (p <0.0001).
Eurosafe also evaluates of drug binding to microsomal proteins and cells in order to evaluate free fraction (fumic, fuhep) and also to predict hepatic clearance or drug-drug interaction potential in vivo, utilizing in vitro microsomal metabolic data.
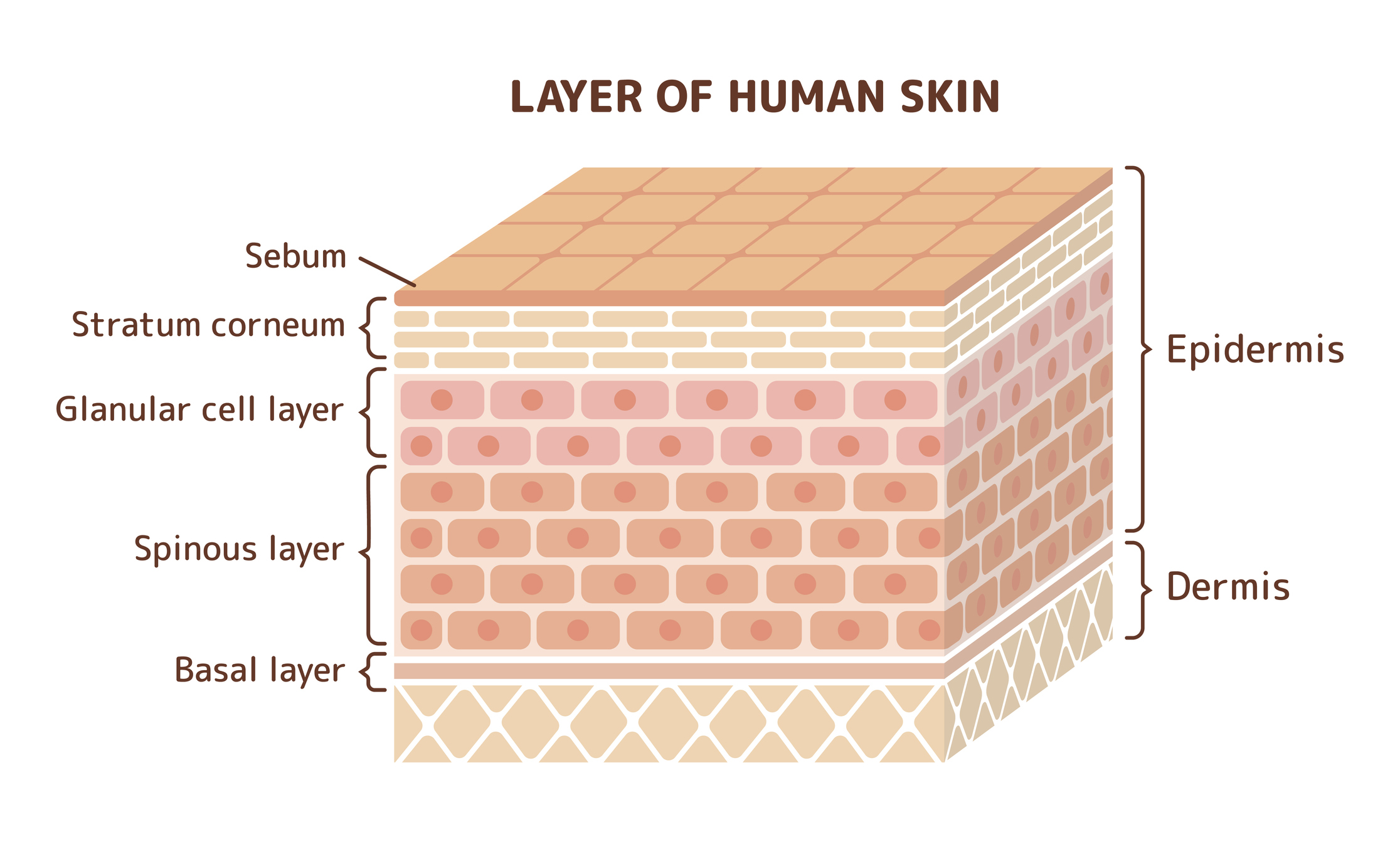
Evaluation of the demal absorption and delivery of a test substance using excised skin
In order to evaluate the possibility of peripheral effects during dermal administration of test compounds, it is essential to evaluate these compounds’ potential transcutaneous passage.
In vitro methods measure the diffusion of chemicals across skin into a fluid reservoir.
Cryopreserved skin is used to measure diffusion only, whereas fresh metabolically-active skin is used to simultaneously measure diffusion and skin metabolism.
Such methods have found particular usage as screenings tests for comparing transcutaneous delivery of chemicals from different formulations. These methods also provide useful models for the assessment of percutaneous absorption in humans. Acceptable data from a minimum of four replicates per test preparation are required.
Using appropriate conditions, which are described in the OECD 428 guidelines, absorption of test compounds during a given time interval is measured by analyzing both receptor fluid and the treated skin.
The test compound remaining on the skin’s surface should be considered as absorbed unless it can be conclusively demonstrated that absorption can be determined from receptor fluid values alone.
Analysis of other components (e.g. material washed off the skin or remaining within skin layers) allows for further data evaluation, including total test substance disposition and percentage recovery.
All components of the skin should be analyzed, and recovery should also be determined. This includes rinsing of the donor chamber, skin surface, and the receptor fluid/chamber.
In some cases, the skin may be fractionated into stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis fractions for additional analysis.
Effect of the formulation on transcutaneous absorbtion of a test compound
Permeability assay for predicting the in vivo absorption of drugs across the gut wall by measuring the rate of transport of a compound across the Caco-2 cell line
Caco 2 permeability assay is part of our portfolio of in vitro ADME screening services.
To understand the suitability of a test compound for oral dosing and to predict the absorption of orally-administered drugs, the Caco 2 assay is widely used across the pharmaceutical industry as an in vitro model of the human small intestinal mucosa.
The Caco-2 cell model mimics processes such as transcellular transport, paracellular transport, and some aspects of efflux and active transport. Caco-2 assay is used to predict human intestinal permeability and to investigate drug efflux.
Assessing transport in both directions (apical to basolateral and basolateral to apical) across the cell monolayer yields an efflux ratio.
Monolayers based on Caco-2 cells which express MDR1 and BCRP transporters allow the study of passive permeability, if the test compound functions as substrate or inhibitor of those transporters.
Based on in vitro permeability and solubility data, the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) is a regulatory mechanism through which one can obtain a waiver of clinical bioequivalence studies, also called a biowaiver.
According to 2000 FDA BCS Guidance , compounds that are classified as Class I (highly soluble and highly permeable) are eligible for BCS biowaivers.
In silico studies/Computational toxicology
Our in Silico services expedite processes of prediction of biological properties related to toxicity, activity and ADME.
We perform Physiologically based Pharmacokinetics modelings (PBPK).
Eurosafe offers services for prediction of three dimensional structure of proteins of interest by the homology modeling method using our automated state of art methods.
Homology modeling uses sequence similarity of amino acid residues with the well known 3D structure (by X ray and NMR) to predict structure of unknown protein.
The structural models are validated for quality and further optimized by Molecular Dynamics simulation. Optimized model can be used for molecular docking, macromolecular engineering and drug designing.
Homology modeling service includes:
- Sequence Alignment of Amino acids
- Prediction of 3D model
- Structure validation
- Structure optimization by MD
Eurosafe offers Molecular docking service to discover, the interaction between the protein of interest and ligand by automated high throughput screening algorithm.
It deduces the ligandability of compounds for the protein. We will report binding affinity, ligand conformation search and active site of the proteins.
On demand, the Protein-ligand complex will be further optimized by molecular dynamics simulation for interaction refinement.
Molecular Docking service includes:
- Structure preparation of Protein and Ligand
- Automated docking simulation
- Affinity prediction, ligand pose prediction and active site prediction on proteins
- Protein-ligand complex optimization by MD
Eurosafe QSAR service includes the prediction of relationships between the geometric structure of a chemical compound and biological activity.
We use QSAR methods such as OECD tool box, VEGA, Tox tree for prediction of Skin sensitization potential of the compounds according to OECD guidelines (ENV/JM/MONO(2007)2).
QSAR service includes:
- Biological properties prediction
- Skin sensitization prediction of ingredients
- Skin metabolism and sensitization prediction of ingredients
- Safety assessment of compounds
Eurosafe offers Physicochemical Based PharmacoKinetics (PBPK) modeling service to predict pharmacokinetics modeling of compounds using the validated open source software PK-SIM.
We offer PBPK service for in vitro to to in vivo pharmacological or toxicological experiments interpolation and extrapolation of knowledge between:
Effect of Dose and Exposure duration: e.g., from continuous to discontinuous, or single to multiple exposures.
Effect of Routes of administration: e.g., from inhalation exposures to ingestion.
Study Species and Individuals variation in PharmacoKinetics of compounds.
In vitro to in vivo extrapolation (IVIVE) refers to the qualitative or quantitative transposition of experimental results or observations made in vitro to predicts phenomena in vivo, biological organisms.
Study of Drug Drug Interaction (DDI).
Study of ADME compartmental model predictor of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion.

