DPRA
Le DPRA (Direct Peptide Reactivity Assay) est une évaluation in Chemico du pouvoir sensibilisant par mesure de la réactivité d’un composé avec un peptide de référence.
OCDE 442C
Couvre le Key event 1 (évènement moléculaire)
H-CLAT
Cet test est une méthode pour l’évaluation de la sensibilisation cutanée qui quantifie les changements dans l'expression des marqueurs de surface cellulaire associés au processus d'activation des cellules denditriques (CD86 et CD54).
La méthode h-CLAT utilise la lignée cellulaire THP-1.
A la suite d'une exposition à un ingrédient, les niveaux d'expression mesurés des marqueurs de surface cellulaire, CD86 et CD54, sont utilisés pour favoriser la distinction entre les sensibilisants cutanés et les non sensibilisants.
OCDE 442E
Couvre le Key event 3 (activation des cellules dendritiques)
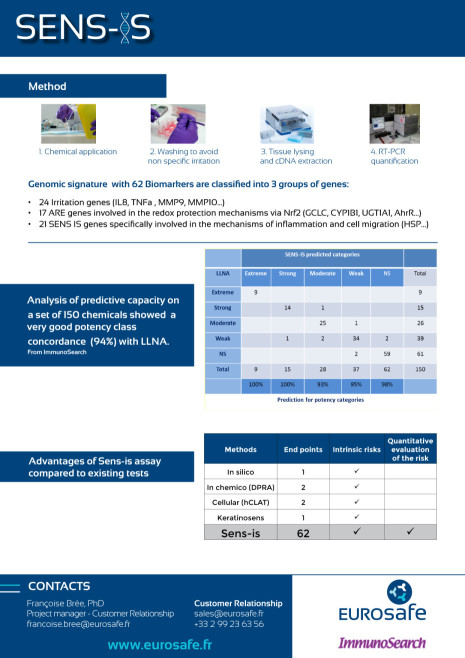
SENS-IS
Le test Sens-IS, développé par Immunosearch, mesure quantitativement la surexpression de 62 biomarqueurs spécifiques de la sensibilisation de la peau, de l’irritation et du système Redox par RT-PCR après application de produits chimiques, mélanges, extraits naturels sur un épiderme humain reconstruit en 3D.
- Réponse qualitative et quantitative
- Distinction de l'irritation et de la sensibilisation
- Epiderme reconstruit 3D : plus proche de la peau donc système biologique complet rendant compte des réponses cellulaires multiples
- Domaine d'application plus large que les autres essais de sensibilisation, possibilité de tester des composés lipophiles
- Bonne concordance avec le LLNA
- Adapté aux produits finis
La validation auprès de l’OCDE est en cours.
Couvre le Key event 2 (activation des kératinocytes)
Retrouvez ci-dessous l'information sur le Sens-IS

GARD™
Eurosafe est le distributeur officiel du test in vitro GARD™ (Senzagen) qui, à partir de lignées de cellules dendritiques, permet d’évaluer la sensibilisation cutanée et, en accord avec les classification CLP/GHS, d’en évaluer sa puissance. Il s’agit d’un test génomique très fiable mesurant les modifications de l’expression de 200 gènes pertinents pour la sensibilisation cutanée (Adverse Outcome Pathways, AOP).
La validation auprès de l’OCDE est en cours. Pour plus d'informations techniques, veuillez consulter le site web SenzaGen.
Retrouvez ci-dessous l'information sur GARD™ Skin
Eurosafe est aussi distributeur officiel du GARD™ air pour la sensiblisation respiratoire.


